Damage Control Surgery Following Endovascular Management in a Patient with Psoas Muscle Penetrating Injury
Article information
본문
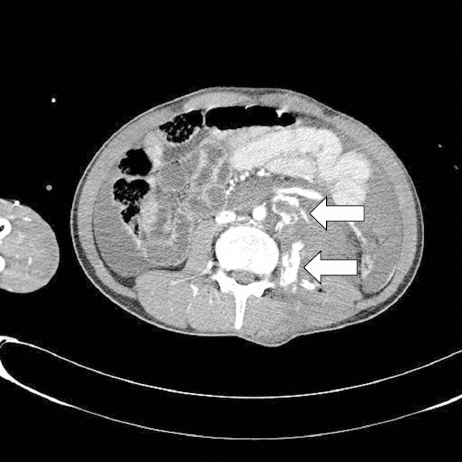
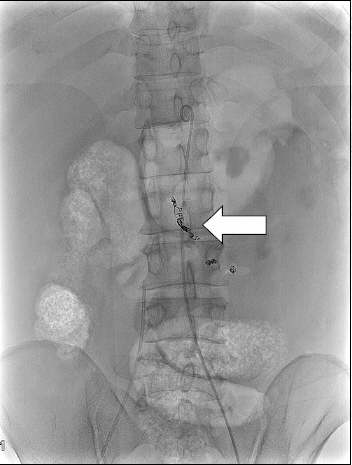
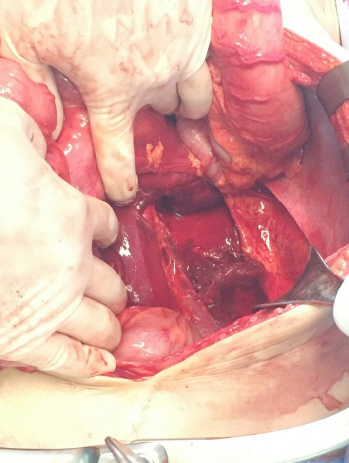
A 50-year-old man was brought to the emergency department after sustaining multiple stab wounds on his back and neck. Systolic blood pressure on arrival was 50 mmHg. A 4-cm regular, oblique, deep wound was found on his left lower back. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a large hemoperitoneum and hemoretroperitoneum, with contrast extravasation from the left psoas muscle (Fig. 1). Angiography and embolization were immediately performed (Fig. 2). Exploratory laparotomy was then performed because of unstable vital signs and abdominal distension after embolization. About 3,000 ml of blood was found in the abdominal cavity; with active bleeding from an injured left psoas muscle that connected with the lower back wound (Fig. 3). Major hemorrhage control was achieved with vessel ligation and diffuse oozing was treated with pad packing. Two days later, take back surgery was performed. He was discharged to home 27 days initial surgery.